The ovarian cycle of dogs
Only one ovarian cycle occurs in bitches during the season (seasonal monoestrous animals). There was once an attempt to systematize the frequency of seasons in bitches throughout the year and classify them as diestrus animals, however, the wide variety of breeds and the variation in the length of the anoestrus (3 – 7 months) does not allow this classification.
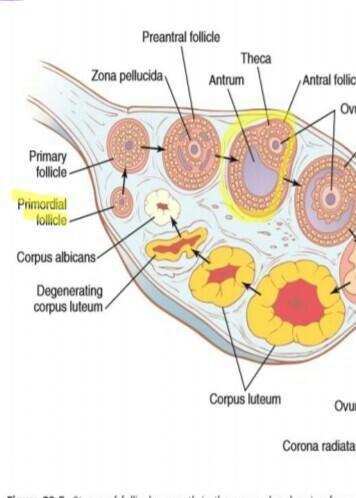
In the course of the ovarian cycle two phases are observed – the follicular phase (growth of ovarian follicles – the so-called “ovarian phase”) and the luteal phase (the so-called “luteal phase”). The follicular phase and the corpus luteal phase. The follicular phase is divided into proestrus and oestrus.
In the proestrus, as a result of FSH stimulation, a pre-ovulatory wave of follicular growth is observed, which, developing in varying numbers, lead to a gradual increase in oestrogen levels and morphological changes within the genital organs such as swelling of the vulva and the vaginal and uterine mucosa, a large amount of bloody discharge is observed (increased permeability of the vaginal mucosal capillaries) containing substances that stimulate and attract males (pheromones). Proestrus in mature bitches lasts 2 – 15, with an average of 9 days. In the final stage of this phase, there is a discharge (peak) of LH, resulting in the production of progesterone and after 72 – 96 hours ovulation occurs. In oestrus, the effect of increasing progesterone levels is observed, i.e. a gradual reduction in the swelling of the mucous membrane (vaginoscopic evidence is the collapse of the mucosal folds and the formation of transverse furrows). The average duration of oestrus in bitches is 9 days, but depending on breed and individual characteristics it can range from 3 to 21 days. Later, the luteal phase develops, which is divided into metoestrus and diestrus. Some authors use these terms interchangeably, but when discussing the ovarian cycle in bitches, distinguishing between these phases seems appropriate.
Metoestrus is the period during which the corpus luteum develops and progesterone production begins, leading to marked changes in the endometrium (in bitches approx. 9 days). During this phase fertilization of the ovum occurs, transport of the embryo through the fallopian tube to the uterus and the initial development of pregnancy. Diestrus is called the inter-uterine phase, during which maximum progesterone levels are observed (the corpus luteum is mature during this period). The uterus is prepared to support and nourish the pregnancy. At the end of this phase, the corpus luteum regresses (approx. 55-70 day of the luteal phase) and a decrease in progesterone levels. In the case of pregnancy, this period overlaps with the moment of birth. The number of layers as well as the shape of the epithelial cells of the vaginal mucosa is hormonally determined. Therefore, any changes in the levels of individual sex hormones, both physiological and pathological, lead to the appearance of characteristic cells. Vaginal cytologic smear evaluation an effective and inexpensive method for imaging the functional status of the genitalia.